The blood gases pH only CPT code is a valuable tool for healthcare professionals seeking to assess a patient’s acid-base balance. This guide delves into the specifics of this code, its applications, and its limitations, providing a comprehensive understanding of its role in clinical practice.
Blood gas analysis measures the pH level of a blood sample, indicating the acidity or alkalinity of the blood. The CPT code associated with this test is crucial for accurate billing and reimbursement.
Blood Gas Analysis: pH Only
Blood gas analysis is a medical test that measures the pH level of blood. pH is a measure of how acidic or alkaline a substance is, and it is important for maintaining the proper function of the body’s cells.
CPT Code, Blood gases ph only cpt code
The CPT code associated with blood gas analysis for pH only is:
- 82365: Blood gas analysis for pH only
Procedure for Blood Gas Analysis: pH Only
Blood Gas Analysis: pH Only measures the pH level of the blood, which indicates the acidity or alkalinity of the blood. This procedure is crucial in assessing the acid-base balance of the body and diagnosing respiratory or metabolic disorders.
Procedure for Collecting Blood Sample
The procedure for collecting a blood sample for pH-only analysis involves the following steps:
- Clean the puncture site with an antiseptic solution to prevent contamination.
- Prick the finger or earlobe with a sterile lancet to obtain a small blood sample.
- Apply pressure to the puncture site to stop bleeding.
- Transfer the blood sample to a pH-specific blood gas analyzer.
Equipment and Materials Required
The equipment and materials required for the procedure include:
- Sterile lancet
- Antiseptic solution
- Blood gas analyzer
- pH-specific blood gas cartridge
Interpretation of pH Results
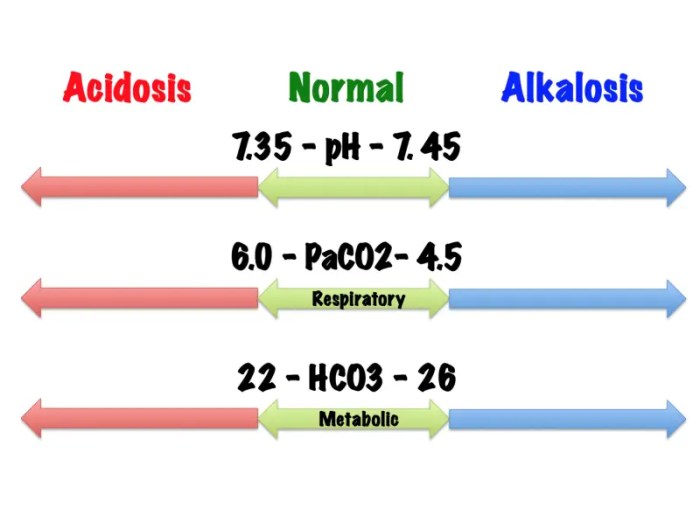
The pH of blood is a critical indicator of the body’s acid-base balance. Understanding the normal range and clinical significance of pH results is essential for healthcare professionals.
Normal Range of pH
The normal pH range in arterial blood is 7.35 to 7.45. This narrow range is tightly regulated by the body’s respiratory and renal systems to maintain homeostasis.
Clinical Significance of Abnormal pH Results
Abnormal pH results can indicate underlying medical conditions that require prompt diagnosis and treatment.
- Acidosis (pH < 7.35):Acidosis occurs when the body accumulates too much acid or loses too much bicarbonate. Conditions that can cause acidosis include diabetic ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, and renal failure.
- Alkalosis (pH > 7.45):Alkalosis occurs when the body accumulates too much bicarbonate or loses too much acid. Conditions that can cause alkalosis include metabolic alkalosis (e.g., excessive vomiting) and respiratory alkalosis (e.g., hyperventilation).
Clinical Applications of Blood Gas Analysis: pH Only
Blood gas analysis, measuring pH alone, has specific clinical applications where it provides valuable information for diagnosis and management. Understanding these applications helps healthcare professionals effectively utilize this test.
Diagnosis of Acid-Base Disorders:pH-only blood gas analysis is primarily used to identify and classify acid-base disorders. By determining whether the pH is acidic, alkaline, or within the normal range, clinicians can differentiate between various types of acid-base imbalances, such as metabolic acidosis, metabolic alkalosis, respiratory acidosis, and respiratory alkalosis.
This information guides appropriate treatment interventions.
Management of Acute Conditions
Respiratory Distress:In acute respiratory distress, pH-only blood gas analysis helps assess the severity of respiratory failure. A low pH indicates respiratory acidosis, which may require mechanical ventilation or other respiratory support. Conversely, a high pH suggests respiratory alkalosis, which may indicate hyperventilation and need for adjustment of ventilator settings.
Cardiopulmonary Arrest:During cardiopulmonary arrest, pH-only blood gas analysis provides crucial information about the patient’s acid-base status. A low pH indicates severe acidosis, which requires immediate resuscitation measures, including defibrillation, chest compressions, and administration of bicarbonate.
Metabolic Disorders:In metabolic disorders, such as diabetic ketoacidosis or lactic acidosis, pH-only blood gas analysis helps monitor the effectiveness of treatment. A gradual increase in pH towards normal values indicates improvement in the underlying metabolic condition.
Monitoring Long-Term Conditions
Chronic Respiratory Disease:In chronic respiratory diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pH-only blood gas analysis helps assess the patient’s respiratory status and response to treatment. A persistently low pH may indicate worsening respiratory function and the need for调整治疗方案。
Metabolic Bone Disease:In metabolic bone diseases, such as renal osteodystrophy, pH-only blood gas analysis is used to monitor acid-base balance and adjust treatment to prevent complications like bone demineralization.
In summary, pH-only blood gas analysis is a valuable tool for diagnosing and managing various clinical conditions, particularly those involving acid-base imbalances. By measuring pH alone, healthcare professionals can effectively assess respiratory function, monitor metabolic disorders, and guide appropriate treatment interventions.
Comparison with Comprehensive Blood Gas Analysis
Blood gas analysis measures the pH, partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2), and partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) in the blood. Comprehensive blood gas analysis additionally includes measurements of bicarbonate (HCO3-), base excess (BE), and oxygen saturation (SaO2).
pH-only blood gas analysis is less expensive and faster than comprehensive blood gas analysis. It is also less invasive, as it requires only a small sample of blood. However, pH-only blood gas analysis provides less information about the patient’s acid-base status than comprehensive blood gas analysis.
Comprehensive blood gas analysis is more expensive and time-consuming than pH-only blood gas analysis. It is also more invasive, as it requires a larger sample of blood. However, comprehensive blood gas analysis provides more information about the patient’s acid-base status than pH-only blood gas analysis.
Understanding blood gases pH levels can be crucial for medical professionals, and the correct CPT code is essential for billing purposes. For students seeking further knowledge, the gizmo answer key 3d eclipse provides valuable insights. Returning to the topic of blood gases pH, it’s important to note that accurate measurement and interpretation are vital for optimal patient care.
When is a Comprehensive Analysis Necessary?
A comprehensive blood gas analysis is necessary when the patient has a complex acid-base disorder or when the pH-only blood gas analysis results are inconclusive. Comprehensive blood gas analysis can also be used to monitor the patient’s response to treatment for an acid-base disorder.
Limitations of pH-Only Blood Gas Analysis: Blood Gases Ph Only Cpt Code
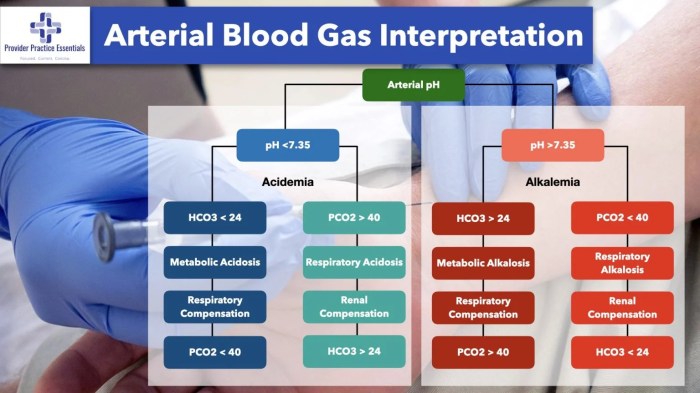
While pH-only blood gas analysis provides valuable information, it has certain limitations. It offers a narrow assessment of acid-base status, which may not always be sufficient for a comprehensive evaluation.
Additional tests or information may be necessary to determine the underlying cause of abnormal pH levels and assess the patient’s overall acid-base balance.
Additional Tests for Comprehensive Assessment
- Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis:Provides a more complete picture of acid-base status, including pH, partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2), partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2), and bicarbonate (HCO3-).
- Electrolyte panel:Measures the levels of electrolytes in the blood, such as sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate, which can influence acid-base balance.
- Lactate measurement:Lactate is a byproduct of anaerobic metabolism and can indicate tissue hypoxia or metabolic acidosis.
- Clinical history and physical examination:Can provide important clues about the underlying cause of acid-base disturbances, such as respiratory or metabolic disorders.
FAQ Explained
What is the CPT code for blood gases pH only?
The CPT code for blood gases pH only is 82355.
What is the normal range for blood pH?
The normal range for blood pH is 7.35 to 7.45.
What are the clinical applications of blood gases pH only analysis?
Blood gases pH only analysis is used to assess acid-base balance in patients with respiratory or metabolic disorders, such as diabetic ketoacidosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.