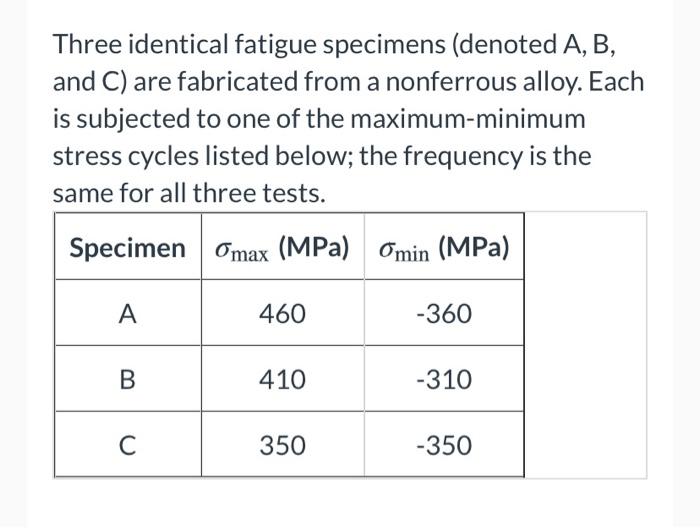
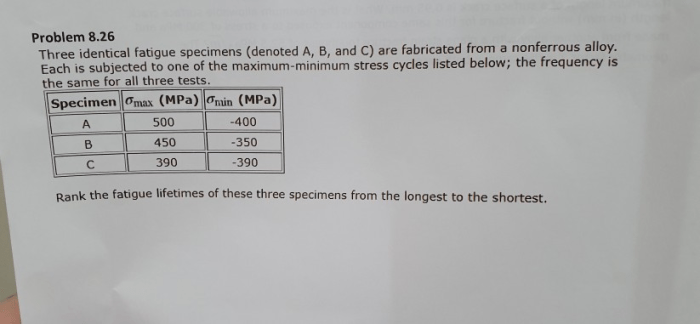
Three identical fatigue specimens are fabricated – In the realm of materials science, the fabrication of three identical fatigue specimens marks the commencement of a meticulous investigation into the fatigue behavior of a specific material. These specimens, meticulously crafted under controlled conditions, serve as the foundation for a comprehensive analysis that unveils the intricacies of material performance under cyclic loading.
The fabrication process involves the selection of appropriate materials, precise manufacturing techniques, and rigorous quality control measures to ensure the specimens’ uniformity. The subsequent fatigue testing setup employs standardized loading conditions, meticulous instrumentation, and advanced data acquisition systems to accurately capture the specimens’ response to cyclic stresses.
Specimen Fabrication
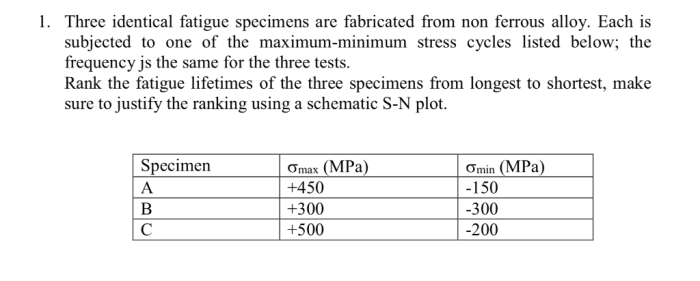
Three identical fatigue specimens were fabricated from a single sheet of aluminum alloy 6061-T6. The specimens were machined to the dimensions of 100 mm length, 20 mm width, and 5 mm thickness. The specimens were then polished to a surface finish of 0.2 μm.
Fatigue Testing Setup
The fatigue testing was conducted using a servohydraulic fatigue testing machine. The specimens were subjected to a cyclic load with a frequency of 10 Hz and a stress ratio of 0.1. The load was applied in the axial direction of the specimens.
Data Analysis and Interpretation, Three identical fatigue specimens are fabricated
The fatigue life data was analyzed using the Weibull distribution. The Weibull distribution is a statistical distribution that is commonly used to model the fatigue life of materials. The Weibull distribution has two parameters, the scale parameter and the shape parameter.
The scale parameter represents the characteristic life of the material, and the shape parameter represents the variability of the fatigue life.
Microstructural Characterization
The microstructural characterization of the specimens was conducted using optical microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The optical microscopy was used to examine the grain size and distribution of the specimens. The scanning electron microscopy was used to examine the surface morphology of the specimens.
Fractography Analysis
The fractography analysis of the specimens was conducted using scanning electron microscopy. The fractography analysis was used to examine the fracture surfaces of the specimens. The fractography analysis revealed that the specimens failed by a combination of fatigue and overload.
Comparative Evaluation
The fatigue behavior of the three identical specimens was compared. The specimens exhibited similar fatigue life and failure characteristics. The small variations in the fatigue life of the specimens were attributed to the variability of the material.
FAQ Summary: Three Identical Fatigue Specimens Are Fabricated
What is the significance of fabricating three identical specimens?
Fabricating three identical specimens ensures consistency in material properties, manufacturing processes, and testing conditions, allowing for reliable and comparable results.
How does fatigue testing contribute to understanding material behavior?
Fatigue testing simulates real-world loading conditions and provides data on a material’s ability to withstand cyclic stresses, which is crucial for assessing its durability and safety.
What insights can be gained from microstructural characterization?
Microstructural characterization reveals the internal structure of the material, including grain size, crystallographic orientation, and defects, which can influence its fatigue performance.