Cellular respiration vs photosynthesis worksheet – Embark on a captivating journey with our Cellular Respiration vs. Photosynthesis Worksheet, a comprehensive guide that delves into the intricacies of these fundamental biological processes. Explore the key differences, reactants, products, stages, and environmental implications of these vital mechanisms that sustain life on Earth.
From the cellular intricacies of energy production to the global impact on climate change, this worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of cellular respiration and photosynthesis, equipping you with a deeper understanding of their significance.
Overview of Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis: Cellular Respiration Vs Photosynthesis Worksheet
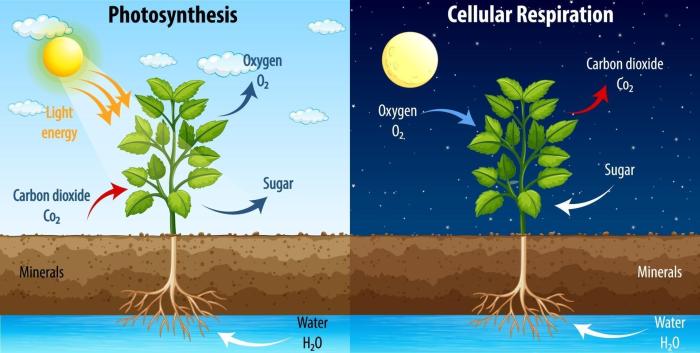
Cellular respiration and photosynthesis are fundamental processes that sustain life on Earth. Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms convert organic molecules into energy, while photosynthesis is the process by which plants and other organisms use sunlight to create organic molecules from inorganic compounds.
The key difference between cellular respiration and photosynthesis is the source of energy. Cellular respiration relies on organic molecules as its energy source, while photosynthesis utilizes light energy. Additionally, cellular respiration releases carbon dioxide as a waste product, while photosynthesis consumes carbon dioxide as a reactant.
Reactants and Products, Cellular respiration vs photosynthesis worksheet
Cellular Respiration:
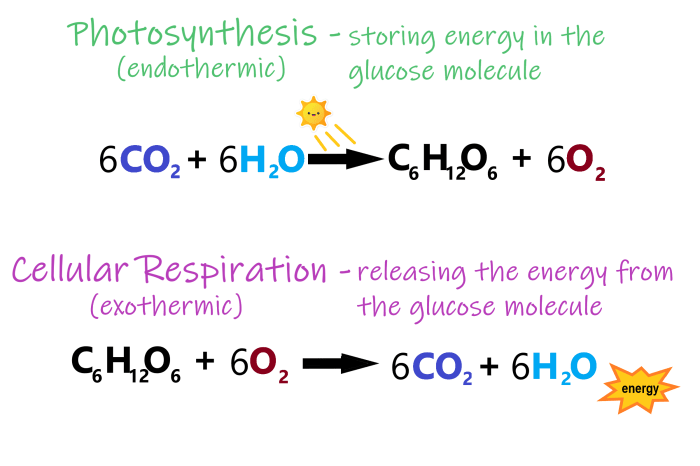
- Reactants: glucose (C6H12O6), oxygen (O2)
- Products: carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), energy (ATP)
Photosynthesis:
- Reactants: carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), sunlight
- Products: glucose (C6H12O6), oxygen (O2)
Stages of Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration occurs in three main stages:
- Glycolysis:Glucose is broken down into two pyruvate molecules, releasing energy in the form of ATP.
- Krebs Cycle:Pyruvate is further broken down, releasing more ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
- Oxidative Phosphorylation:NADH and FADH2 are used to generate a proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane, which drives the production of ATP.
Stages of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis occurs in two main stages:
- Light-Dependent Reactions:Sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll, which generates ATP and NADPH.
- Calvin Cycle:ATP and NADPH are used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
Energy Production and Consumption
Cellular respiration generates ATP, the energy currency of the cell. The energy released during the breakdown of glucose is captured and stored in ATP molecules, which are then used to power cellular activities.
Photosynthesis utilizes light energy to produce glucose, a primary energy source for organisms. The glucose produced during photosynthesis is used for cellular respiration or stored as starch for later use.
Location and Importance
Cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. It is essential for providing energy to the cell and maintaining cellular functions.
Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells. It is crucial for producing food for plants and other organisms and releasing oxygen into the atmosphere.
Environmental Implications
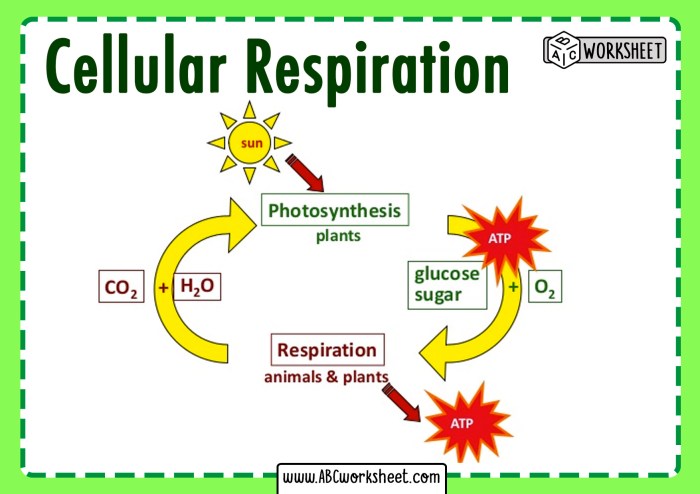
Cellular respiration and photosynthesis contribute to the carbon cycle and oxygen production.
Cellular respiration releases carbon dioxide, which is used by plants for photosynthesis. Photosynthesis consumes carbon dioxide and releases oxygen, which is essential for aerobic respiration.
The balance between cellular respiration and photosynthesis is crucial for maintaining the Earth’s atmosphere and regulating climate change.
Key Questions Answered
What is the primary difference between cellular respiration and photosynthesis?
Cellular respiration consumes organic molecules to produce energy, while photosynthesis uses light energy to synthesize organic molecules.
What are the three main stages of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
How does photosynthesis contribute to the carbon cycle?
Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and converts it into organic molecules, which are then released back into the atmosphere through cellular respiration.