Hierarchy of needs of geriatric patients – Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is a foundational concept in psychology that describes the stages of human needs, from basic physiological requirements to self-actualization. This framework is particularly relevant to geriatric care, as the needs of older adults often differ from those of younger populations.
Understanding and addressing these needs is crucial for promoting the well-being and quality of life of geriatric patients.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore each level of Maslow’s hierarchy as it pertains to geriatric patients, discuss the challenges and opportunities associated with meeting these needs, and provide practical strategies for healthcare professionals and caregivers.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs in Geriatrics: Hierarchy Of Needs Of Geriatric Patients
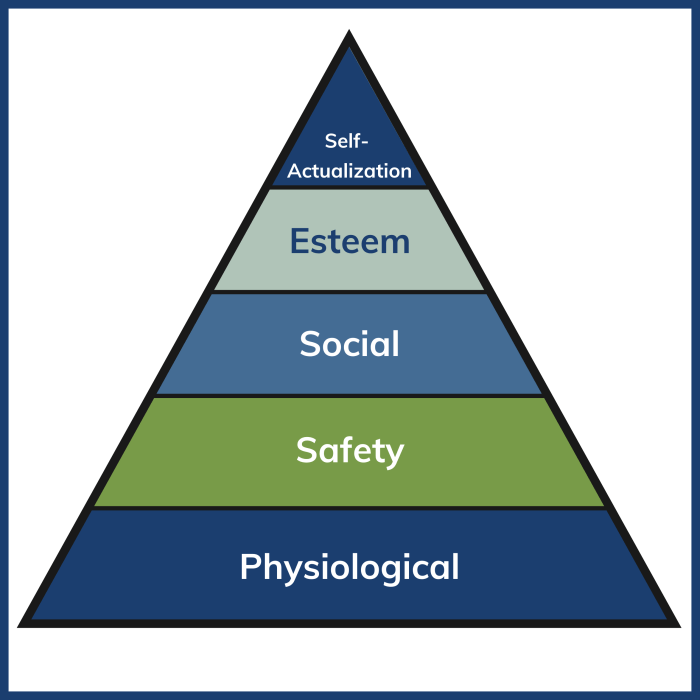
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is a psychological theory that suggests that human beings have a set of needs that must be met in order to achieve optimal well-being. The hierarchy is typically depicted as a pyramid with five levels, with the most basic needs at the bottom and the most complex needs at the top.
The five levels of the hierarchy are:
- Physiological needs
- Safety and security needs
- Love and belonging needs
- Esteem needs
- Self-actualization needs
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is relevant to geriatric patients because it can help healthcare professionals understand the needs of older adults and develop interventions to meet those needs. As individuals age, their needs may change, and the hierarchy may need to be adapted to reflect these changes.
Physiological Needs
Physiological needs are the most basic needs that must be met for survival. These needs include food, water, shelter, and sleep. In geriatric patients, physiological needs may be more difficult to meet due to age-related changes in metabolism, mobility, and cognitive function.
Healthcare professionals can help meet the physiological needs of geriatric patients by providing nutritious meals, ensuring access to clean water, and creating a safe and comfortable environment.
- Providing nutritious meals
- Ensuring access to clean water
- Creating a safe and comfortable environment
Safety and Security Needs, Hierarchy of needs of geriatric patients
Safety and security needs are the need for protection from harm and the need for a sense of stability and predictability. In geriatric patients, safety and security needs may be increased due to age-related changes in physical and cognitive function.
Healthcare professionals can help meet the safety and security needs of geriatric patients by creating a safe environment, providing supervision and assistance, and ensuring access to healthcare and social services.
- Creating a safe environment
- Providing supervision and assistance
- Ensuring access to healthcare and social services
FAQ Guide
What are the physiological needs of geriatric patients?
Physiological needs include basic necessities such as food, water, shelter, sleep, and medical care. As individuals age, their physiological needs may change, requiring specific attention to dietary modifications, mobility assistance, and medication management.
How can love and belonging needs be fostered in geriatric patients?
Love and belonging needs can be met through social connections, meaningful relationships, and a sense of community. Healthcare professionals can encourage family involvement, facilitate group activities, and support volunteer opportunities to promote social engagement and combat loneliness.
What is the role of self-actualization in geriatric care?
Self-actualization involves the pursuit of personal growth, fulfillment, and purpose. For geriatric patients, this may involve engaging in hobbies, learning new skills, or volunteering. Healthcare professionals can support self-actualization by encouraging participation in meaningful activities and providing opportunities for personal expression.